
Clinical Study
In order to allow more patients to use our product safely
and comfortably, we conducted lots of clinical research. The latest clinical trial by International Diabetic Federation WPR president Dr Ji was shown in
American Diabetic Association conference in July 2019, and was published in a branch journal of the Lancet.

In conclusion, our study indicates that an insulin jet
injector is more effective than an insulin pen in improving plasma glucose and
insulin levels in type 2 diabetic patients. Furthermore, the jet injector is easy to operate with high acceptance and
tolerance observed in the investigated cohort.

In conclusion, lispro administered by the QS-M needle-free
injector results in an earlier and higher insulin exposure than the
conventional pen, and a greater early glucose-lowering effect with similar
overall potency. Enhanced insulin absorption by jet injection mainly occurred
during the early period after administration. It closely resembles the
pattern of endogenous early-phase insulin secretion. The improved pro-files of
lispro by jet injection might better mimic the physio-logical postprandial
insulin secretion.
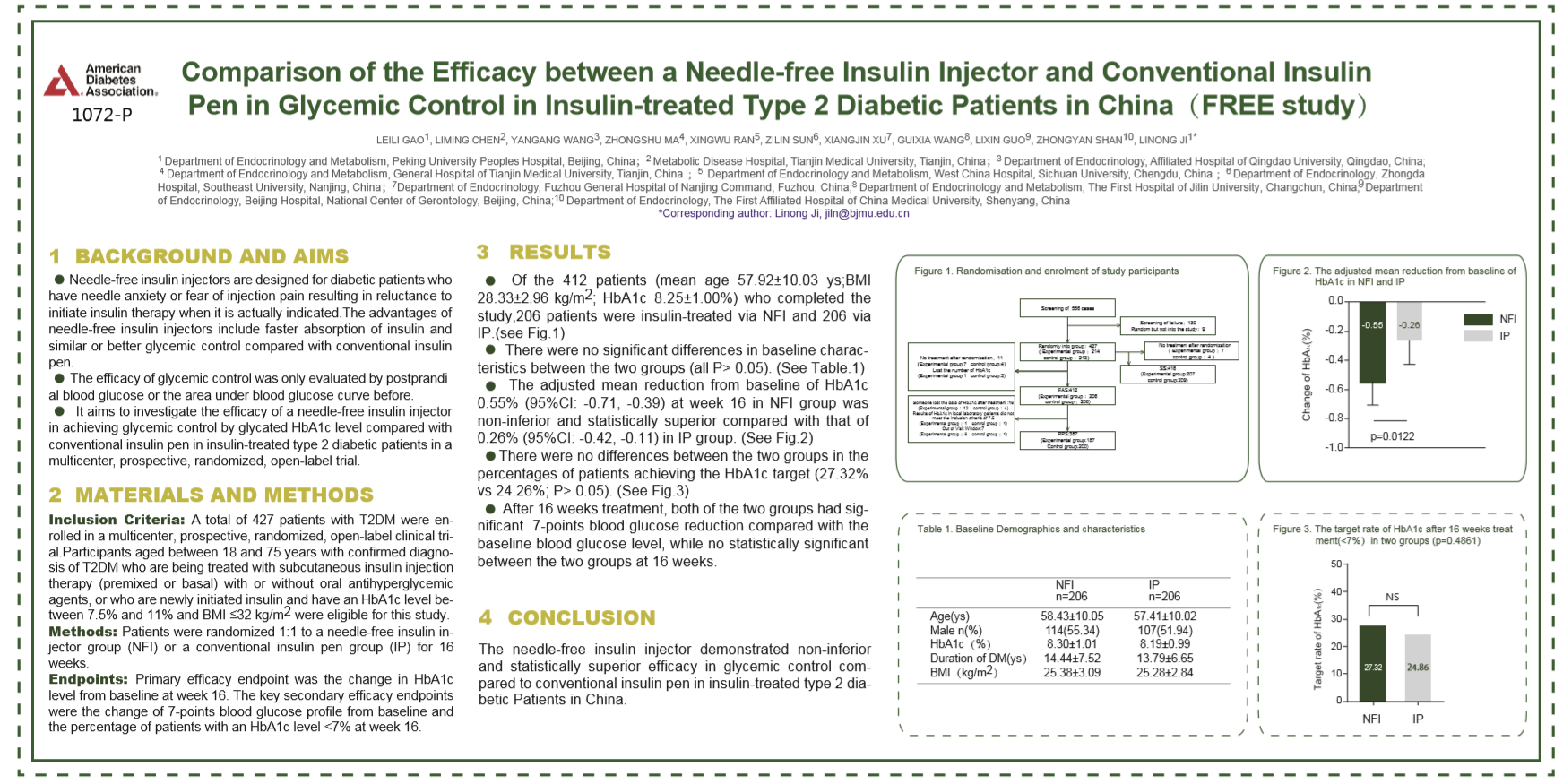
The needle-free insulin injector demonstrated non-inferior
and statistically superior efficacy in glycemic control compared to
conventional insulin pen in insulin-treated type 2 diabetic patients in China.
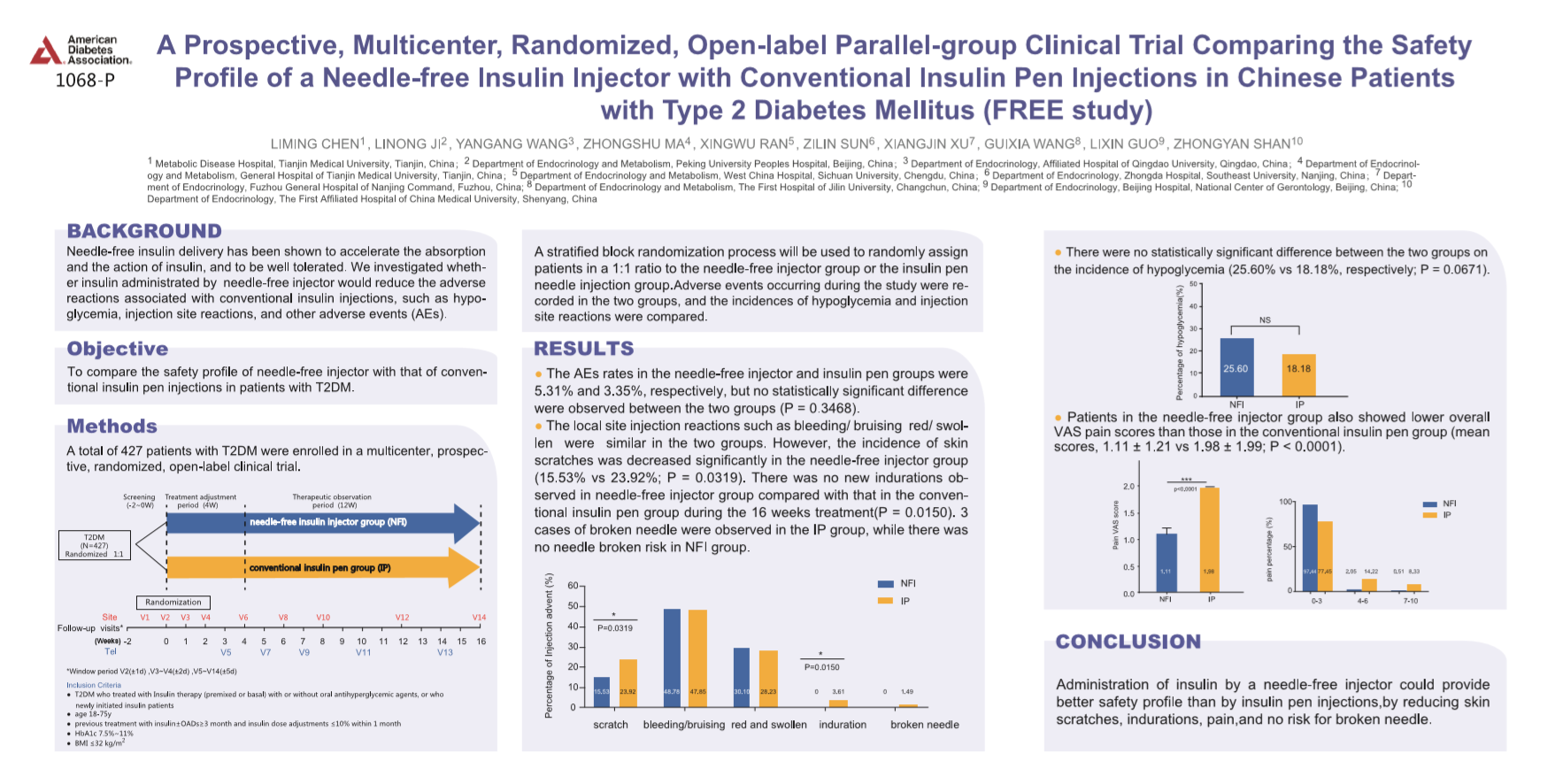
Administration of insulin by a needle-free injector could
provide better safety profile than by insulin pen injections, as it can reduce skin
scratches, indurations, pain and risks of broken needle.
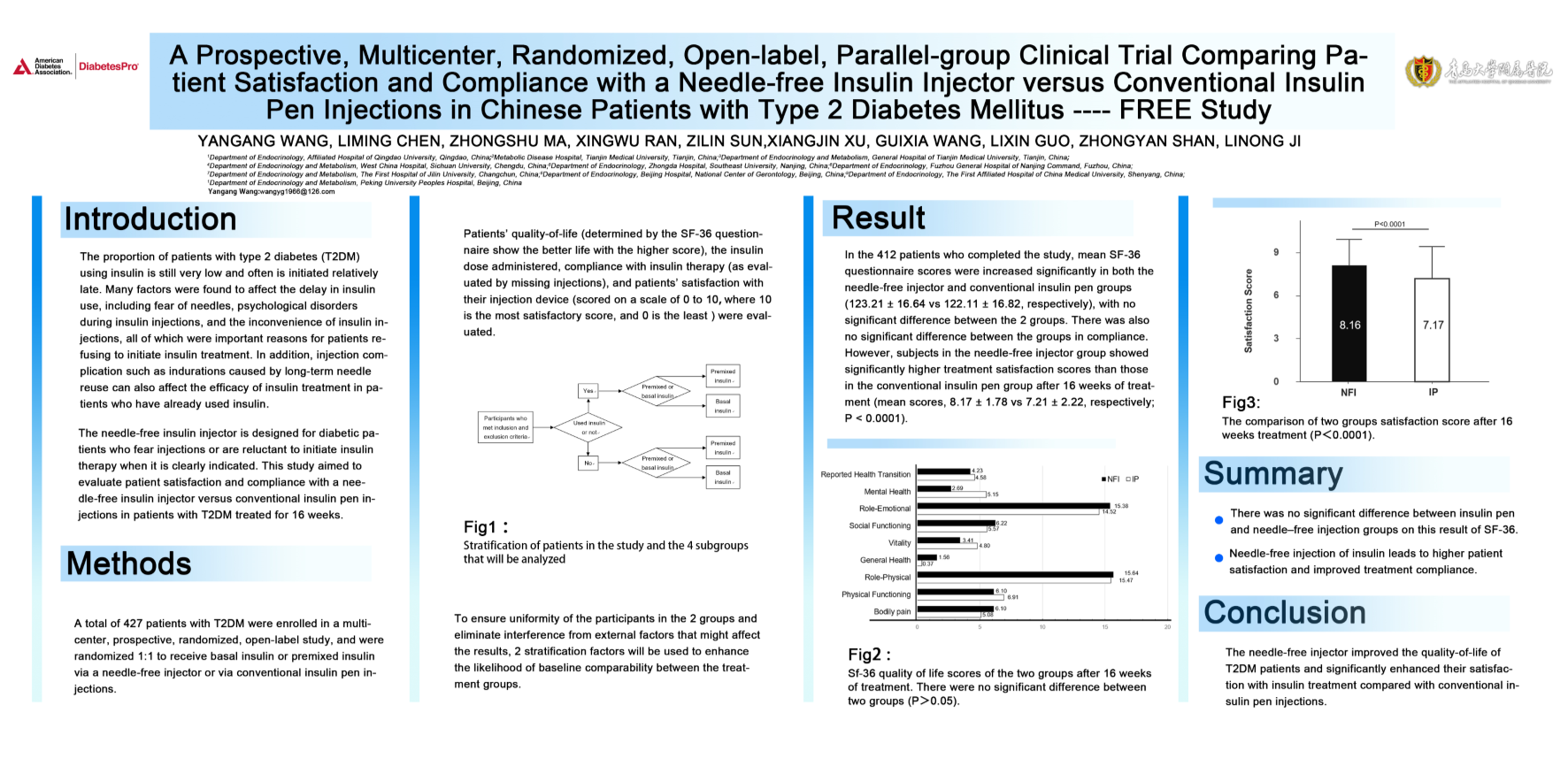
The needle-free injector improved the quality-of-life of
T2DM patients and significantly enhanced their satisfaction with insulin
treatment compared with conventional insulin pen injections.

Insulin therapy through needle-free injector showed a
non-inferior glycemic-lowering effect and a significantly enhanced level of
patient satisfaction with insulin treatment compared with conventional insulin
therapy through needle injections. In addition, the needle-free injector also
had a better safety profile.

The result shows that needle-free jet injection of insulin
glargine was more effective than use of an insulin pen for good glycemic
control in patients with T2DM.
